Calculation plastic container


Introduction
The behavior of plastics and the computational description is not trivial. If one assumes linear elastic behavior, this may still fit to some extent for some plastics with glass fiber content such as PA6 GF30, but this is no longer the case for a material such as PE-LLD, which is used, for example, in wastewater tanks.
In addition to the nonlinearity of the material behavior, the geometrically nonlinear behavior must also be taken into account. Table values from conventional databases such as Campus are often no longer sufficient here. If temporally nonlinear behavior such as creep and relaxation is added, measurements on samples of the material used are often necessary in order to perform good simulations.
Task / Calculation
The tank of the new development of a wastewater lifting unit was to be optimized. In addition to the pressure load of 0.5 bar overpressure, creep effects occur due to heating with warm wastewater. These may cause the screw connections to loosen or the tank to leak.
The tank is manufactured by the centrifugal method, so that the wall thicknesses are subject to a certain tolerance. Experiments require that appropriate molds be built. Therefore, a simulation-driven development approach should be adopted. The material properties were measured on corresponding samples at different temperatures and fitted with material models. Merkle & Partner coordinated the tests at the corresponding testing institutes. Likewise, damage criteria were developed with the comparison of test results. The calculations of the previous models were compared with test results and showed very good agreement even for the bursting load case.
Result
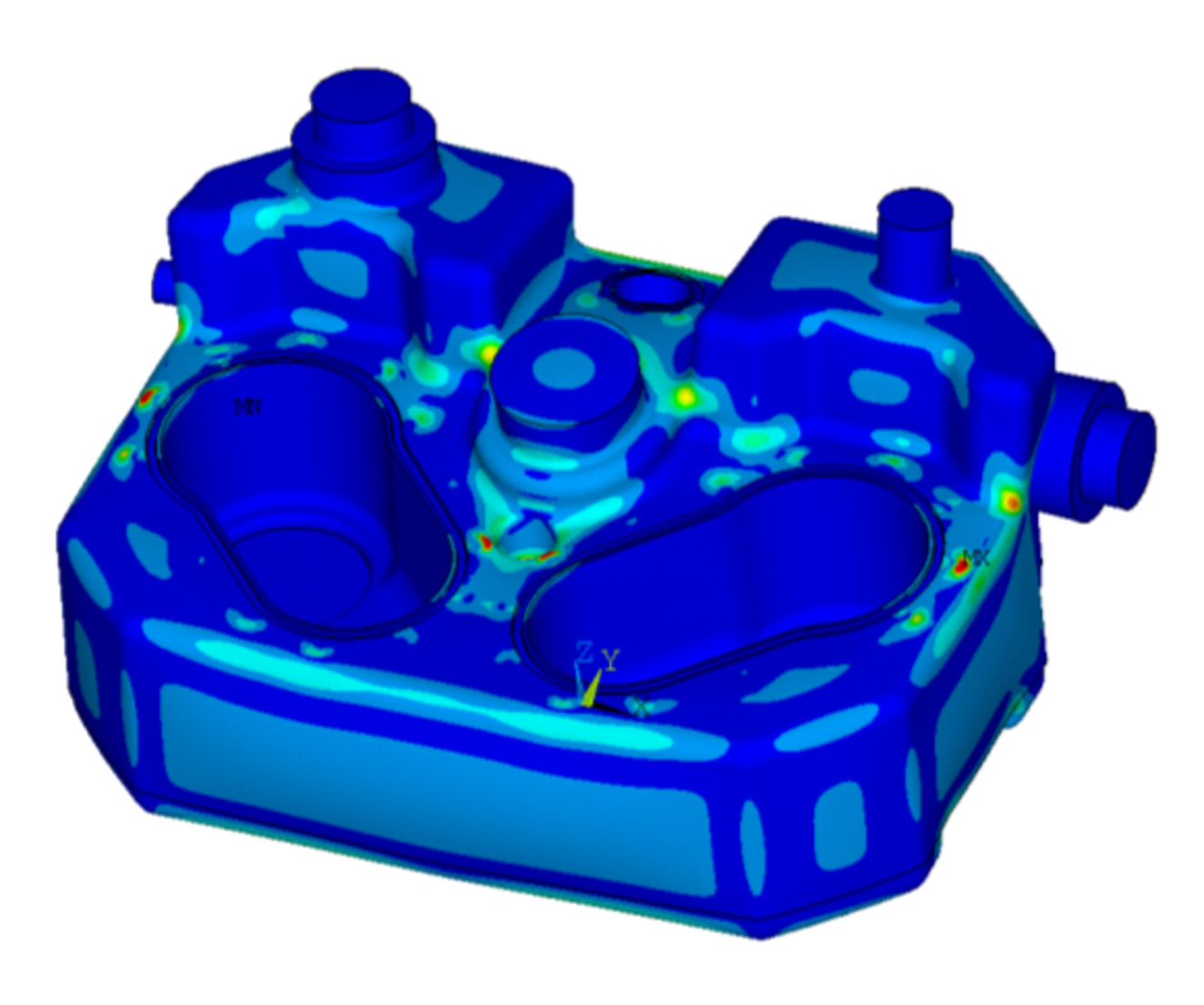
The recalculation of the previous variant showed good to very good agreement between the burst tests and the creep tests. In the bursting test, both the bursting pressure and the damage pattern were very well matched. The creep tests at elevated temperatures also showed sufficiently good agreement.
The new development could now be carried out without time-consuming prototype grinding on the basis of simulation variants. The final tests on the final container showed that all requirements could be met. The simulation thus helped to carry out this and future developments much faster, thus saving time and costs.
Keywords
- Waste water tank
- Bursting load
- Burst test
- Geometrically nonlinear behavior
- Creep
- Plastic
- Nonlinear behavior
- PE-LLD
- Damage criterion
- Simulation
- Temperature dependence
- Relaxation
- Test
- Creep strength
With kind permission of KSB Pegnitz